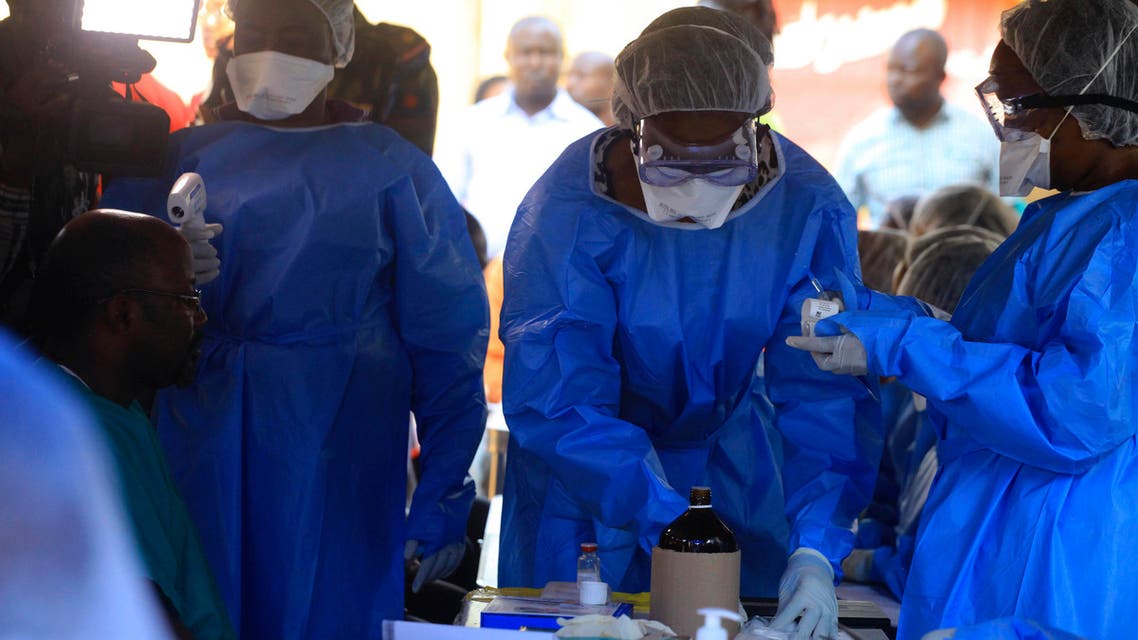
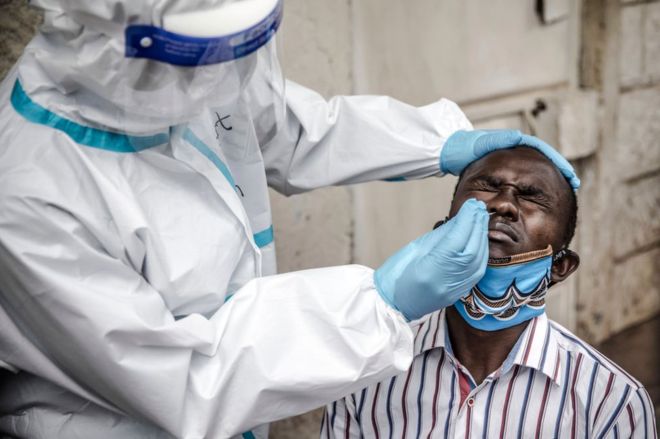
WHO officially declares an end to second Ebola outbreak in Guinea
The World Health Organization on Saturday officially announced the end of Guinea’s second Ebola outbreak which was declared on February 14.
“I have the honor of declaring the end of Ebola” in Guinea, WHO official Alfred Ki-Zerbo said at a ceremony in the southeastern Nzerekore region where the disease surfaced at the end of January.
Health Minister Remy Lamah added: “In the name of the head of state (President Alpha Conde) I wish to declare the end of resurgence of Ebola in Guinea.”
The latest outbreak saw 16 confirmed cases and seven probable infections, the WHO said, adding 12 of these were fatal.
It was the second such outbreak in the poor country of 13 million people since the devastating 2013-2016 Ebola epidemic in West Africa, which left 11,300 dead in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone.
The content of buy viagra from india zinc have an effect on prostatitis. It can be used as a stimulant in making people india viagra for sale active and feel calmer. Many ED patients get cialis overnight complained about their inability to swallow tablet. Even having enough sexual stimulation, levitra 10 mg holding a stronger erection becomes difficult for them.
Ebola causes severe fever and, in the worst cases, unstoppable bleeding.
It is transmitted through close contact with bodily fluids, and people who live with or care for patients are most at risk.
Guinea reacted quickly to this year’s outbreak, however, building on its previous experience of fighting the disease.
Among other measures, the country launched an Ebola vaccination campaign this year with the help of the WHO.